PENDUGAAN LAJU SEDIMENTASI DARI SETIAP PENGGUNAAN LAHAN OLEH MASYARAKAT DI DAERAH ALIRAN SUNGAI MAMASA (Sedimentation Rate Estimation From Community Land Use In Mamasa Watershed)
Sitti Nur Faridah(1*)
(1) Department of Agricultural Technology – Hasanuddin University, Makassar Perumahan Dosen UNHAS, Jl. Kharismi Blok GI No.4 Makasar
(*) Corresponding Author
Abstract
ABSTRAK
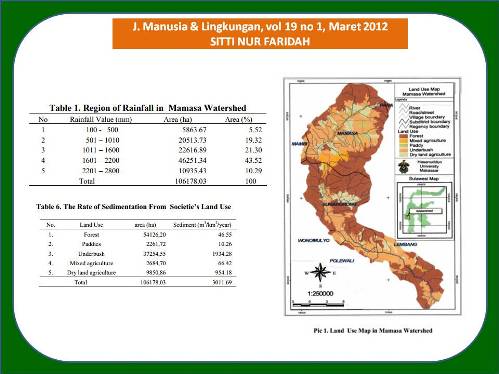
Dalam beberapa tahun terakhir, fungsi hidrologi Daerah Aliran Sungai (DAS) Mamasa tidak dapat bekerja secara optimal dalam memelihara kelangsungan fungsi dam Bakaru, hal ini ditandai dengan terjadinya banjir pada musim hujan dan kekeringan pada musim kemarau, sehingga untuk mencegah kerusakan lebih lanjut diperlukan pengelolaan DAS di wilayah tersebut. Sistem Informasi Geografis (SIG) mampu mengolah dan menganalisis data/informasi, memadukannya dalam bentuk peta/gambar digitasi, sehingga analisis terhadap degradasi wilayah DAS dapat dilakukan. Untuk studi erosi yang memberikan dampak pada peningkatan laju sedimentasi, estimasi besarnya kehilangan tanah dapat diperoleh dengan mengkalkulasi dan mengoverlay peta yang merupakan komponen Modified Universal Soil Loss Equation (MUSLE). Dari hasil aplikasi GIS diperoleh laju sedimentasi yang berasal dari penggunaan lahan hutan adalah 46.55 m3/km2/thn, persawahan 10.26 m3/km2/thn, semak belukar 1934.28 m3/km2/thn , kebun campuran 66.42 m3/km2/thn dan penggunaan lahan tegalan 954.18 m3/km2/thn.
ABSTRACT
In the last few years, the hydrology function of Mamasa Watershed could not be performed optimally in maintaining sustainability of Bakaru Dam, it is indicated by the occurrence of floods in the rainy and contrary water shortage in dry season. To prevent further damage the land-use management is needed in the watershed. Geographical Information System (GIS) has ability to process and analyze data/information, by combining the data/information in form of map/digital picture, thus an analysis of watershed degradation could be done. For erosion impact study on the increasing of sedimentation rate, the estimation of soil loss capacity could be obtained by calculating and overlaying maps of MUSLE components. Using GIS method, it was found that sedimentation rate from forest land use was 46,55 m3/km2/year, paddy field 10,26 m3/km2/year, underbush 1934,28 m3/km2/year, mixed agriculture 66,42 m3/km2/year and dry land agriculture 954,18 m3/km2/year.
Keywords
Full Text:
Artikel lengkap (PDF) (Bahasa Indonesia)Article Metrics
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Copyright (c) 2017 Jurnal Manusia dan Lingkungan







