ISOLASI, SKRINING DAN IDENTIFIKASI JAMUR XILANOLITIK LOKAL YANG BERPOTENSI SEBAGAI AGENSIA PEMUTIH PULP YANG RAMAH LINGKUNGAN (Isolation, Screening and Identification Xylanolytic Local Fungi that Potentially as Pulp Bleaching Agents)
Elisa Nurnawati(1*), Sebastian Margino(2), Erni Martani(3), Sarto Sarto(4)
(1) Jurusan Biologi, Fakultas MIPA, Universitas Sriwijaya, Indralaya, Sumatera Selatan 30662
(2) Laboratorium Mikrobiologi, Fakultas Pertanian, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Bulaksumur, Yogyakarta 55281
(3) Laboratorium Mikrobiologi, Fakultas Pertanian, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Bulaksumur, Yogyakarta 55281
(4) Jurusan Teknik Kimia, Fakultas Teknik, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Sekip, Yogyakarta 55281
(*) Corresponding Author
Abstract
ABSTRAK
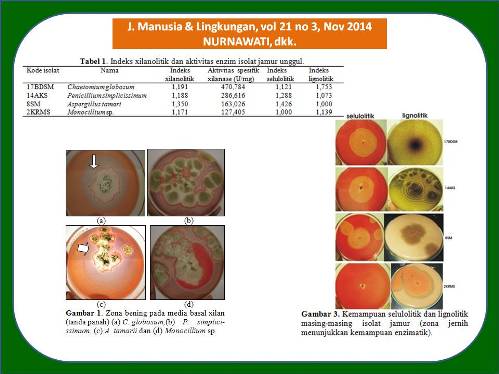
Xilanase merupakan enzim yang berfungsi luas dalam bidang industri. Xilanase digunakan sebagai perlakuan awal proses pemutihan kertas di industri pulp dan kertas sehingga dapat mengurangi penggunaan senyawa klorin yang berbahaya bagi lingkungan. Xilanase yang cocok digunakan dalam industri pulp dan kertas seharusnya bebas dari aktivitas selulase. Jamur merupakan salah satu kelompok mikrobia yang mampu menghasilkan xilanase. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk memperoleh isolat jamur unggul lokal penghasil xilanase dari tanah yang diasumsikan memiliki kandungan xilan tinggi. Tanah di sekitar industri pulp dan kertas; hutan akasia di Kab. Muara Enim dan Ogan Ilir, Sumatera Selatan; hutan Wanagama, Yogyakarta; penggergajian kayu di kota Palembang dan Yogyakarta serta TPA Palembang digunakan sebagai sumber isolat jamur. Berdasarkan skrining awal dalam media basal xilan agar diketahui bahwa dari 111 isolat jamur yang diperoleh, sebagian besar mempunyai potensi menghasilkan xilanase, akan tetapi hanya 12 isolat yang mempunyai kemampuan xilanolitik tinggi. Skrining selanjutnya dilakukan pada media basal xilan cair menunjukkan bahwa jamur yang diidentifikasi sebagai Chaetomium globosum, Penicillium simplicissimum, Aspergillus tamarii dan Monocillium sp. berpotensi unggul dalam menghasilkan xilanase dibandingkan isolat lainnya berdasarkan aktivitas enzim spesifiknya. Keempat jamur tersebut diketahui juga memiliki aktivitas lignolitik dan selulolitik. Oleh karena itu, xilanase yang diproduksi ke empat jamur tersebut berpotensi dikembangkan sebagai agen pemutih pulp.
ABSTRACT
Xylanase has great potential for industry application. Application of xylanase can be done in pretreatment of pulp bleaching in the pulp and paper industry. Enzyme application can reduce the use of chlorine compounds that are harmful to the environment. Therefore, xylanase that used in pulp bleaching should be free of cellulase activity. Fungi are one of the groups of microbes that are able to produce xylanase. The aims of this study was to obtain local xylanase-producing fungal isolates from soil that assumed contain of xylan. The source of fungal isolates were the soil around the pulp and paper industry; Acacia forests in the district Ogan Ilir and Muara Enim, South Sumatra; Wanagama, Yogyakarta; sawmills in Palembang and Yogyakarta; and Palembang landfill. Based on the initial screening in the agar basal medium, 111 fungal isolates were obtained. Most of them were the xylanase-producing fungi, but only 12 fungal isolates that have high xylanolytic capabilities. Further screening was performed on xylan liquid basal medium. The results showed that the fungus identified as Chaetomium globosum, Penicillium simplicissimum, Aspergillus tamarii and Monocillium have higher xylanase specific activity than the other isolates. They were also have lignolytic and cellulolytic activities. Therefore, fungal xylanase potentially developed as a pulp bleaching agent.Keywords
Full Text:
Artikel lengkap (PDF) (Bahasa Indonesia)References
Angayarkanni, J., Palaniswamy, M., Pradeep, B.V. dan Swaminathan, K. 2006. Biochemical Substitution on Fungal Xylanases for Prebleaching of Hardwood Kraft Pulp. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 5(10):921929.
Assamoi, A.A, Delvigne, F., Aldric, J., Destain, J. dan Thonart, P. 2008. Improvement of Xylanase Production by Penicillium canescens 10-10c in Solid-State Fermentation. BASE. 12(2):111-118.
Bailey, M.J., Biely, P. dan Poutanen, K. 1992. Interlaboratory Testing of Methods for Assay of Xylanase Activity. J. Biotech. 23:257–270.
Guimarães. L.E.S, Peixoto-Nogueira, S.C., Michelin, M., Rizzatti, A.C.S., Sandrim, V.C., Zanoelo, F.F., Aquino, A.C.M.M., Junior, A.B. dan Polizeli, M.L.T.M. 2006. Screening of Filamentous Fungi for Production of Enzymes of Biotechnological Interest. Brazilian J. Microbiol. 37:474-480.
Guimaraes, N.C.A., Sorgatto, M., Peixoto-Nogueira, S.C., Betini, J.H.A., Zanoelo, F.F., Marques, M.R., Polizeli, M.L.T.M. dan Giannesi, G.C.. 2013. Bioprocess and Biotechnology: Effect of Xylanase from Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus flavus on Pulp Biobleaching and Enzyme Production Using Agroindustrial Residues as Substract. SpringerPlus. 2:380–386.
Kar, S., Mandal, A., das Mohapatra, P.K., Mondal, K.C. dan Pati, B.K. 2006. Production of Cellulose-Free Xylanase by Trichoderma reesei SAF3. Brazilian J. Microbiol . 37:462-464.
Knob, A dan Carmona, E.C. 2008. Xylanase Production by Penicillium sclerotiorum and Its Characterization. World Appl. Sci. J. 4(2):277–283.
Lemos, J.L.S., Bon, E.P.S., Santana, M.F.E. dan Junior, N.P. 2000. Thermal Stability of Xylanases Produced by Aspergillus awamori. Brazillian J. Microbiol. 31(3):206-211.
Muthezhilan, R., Ashok, R. dan Jayalakshmi, S. 2007. Production and Optimization of Thermostable Alkaline Xylanase by Penicillium oxalicum in Solid STATE fermentation. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 6:020028.
Nair, S.G., R. Sindhu dan S. Shashidar. 2008. Fungal Xylanase Production Under Solid State and Sub-Merged Fermentation Conditions. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2:82–86.
Oda, K., Kakizono, D., Yamada, O., Iefuji, H., Akita, O. dan Iwashita, K. 2006. Proteomic Analysis of Extracellular Proteins from Aspergillus oryzae Grown under Submerged and Solid-State Culture Conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72(5):3448–3457.
Pang, P.K. dan Che-Omar, I. 2005. Xylanase Production by Local Fungal Isolate Aspergillus niger USMAI1 via Solid State Fermentation Using Palm Kernel Cake (PKC) as Substrate. Songklanarin J. Sci. Technol. 27(1):325–336.
Pitt, J.I. dan Hocking, A.D. 1997. Fungi and Food Spoilage. Blackie Academic dan Proffesional. London. pp 21–416.
Puspaningsih, N.N.T., Suwito, H., Sumarsih, S., Rohman, A. dan Asmarani, O. 2007. Hidrolisis Beberapa Jenis Xilan Dengan Enzim Xilanolitik Termofilik Rekombinan. Berkala Penelitian Hayati. 12:191194.
Raghukumar, C., Muraleedharan, U., Gaud, V.R. dan Mishra, R. 2004. Xylanases of Marine Fungi of Potential Use for Biobleaching of Paper Pulp. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 31 (9):433441.
Samson, R.A., Hoekstra, E.S. dan Prisvad, J.C. 2004. Introduction to Food and Airborne Fungi. Seventh Edition. Centralbureu voor Schimmelcultures. The Nederlands. pp 389.
Savitha, S., Sadhasivam, M. dan Swaminathan, K. 2007. Application of Aspergillus fumigatus Xylanase for Quality Improvement of Waste Paper Pulp. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 78:217–221.
Subramaniyan, S dan Prema, P. 2002. Biotechnology of Microbial Xylanases : Enzymology, Molecular Biology and Application. Crit. Rev. Biotech. 22(1):33–46.
Sudan R. dan Bajaj, B.K. 2007. Production and Biochemical Characterization of Xylanase from An Alkalitolerant Novel Species Aspergillus niveus RS2. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 23:491–500.
Sunna, A. dan G. Antranikian. 1997. Xylanolytic Enzymes from Fungi and Bacteria. Crit. Rev. Biotech. 17(1):3967.
Article Metrics
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Copyright (c) 2017 Jurnal Manusia dan Lingkungan







