PERENCANAAN SISTEM PENYALURAN AIR LIMBAH DOMESTIK KOTA BOGOR MENGGUNAKAN AIR HUJAN UNTUK DEBIT PENGGELONTORAN (Planning of Domestic Wastewater Sewerage in Bogor City Using Rainwater for Flushing Flowrate)
Allen Kurniawan(1*), Nura Adithia Dewi(2)
(1) Jurusan Teknik Sipil dan Lingkungan, Institut Pertanian Bogor, Kampus IPB Dramaga, Bogor, 16680.
(2) Jurusan Teknik Sipil dan Lingkungan, Institut Pertanian Bogor, Kampus IPB Dramaga, Bogor, 16680.
(*) Corresponding Author
Abstract
ABSTRAK
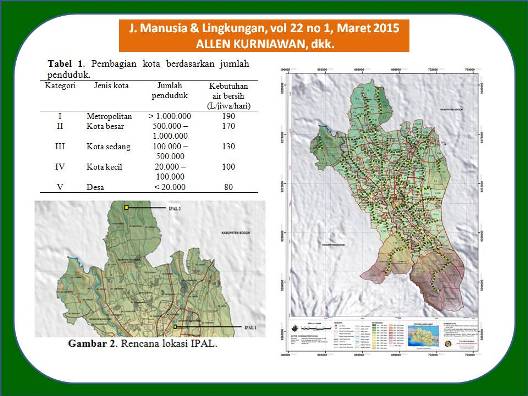
Sistem penyaluran air limbah merupakan bagian penting dalam sistem prasarana perkotaan. Tujuan penelitian ini merancang konfigurasi sistem penyaluran air limbah domestik dan memodifikasi sistem drainase skala mikro di Kota Bogor untuk memenuhi debit penggelontoran. Data penelitian berupa data sekunder dari instansi terkait, studi pustaka, dan hasil beberapa penelitian terdahulu. Perkiraan jumlah penduduk setiap kelurahan pada tahun perencanaan 2035 menggunakan metode geometrik. Instalasi Pengolahan Air Limbah (IPAL) dibangun pada dua lokasi yaitu IPAL 1 di Kelurahan Bantarjati dan IPAL 2 di Kelurahan Mekarwangi. Perencanaan blok pelayanan sebanyak 254 buah dan jumlah manhole sebanyak 334 buah. Perhitungan kebutuhan air bersih menghasilkan nilai debit jam puncak air limbah (Qjp) rata-rata sebesar 5,75 L/detik. Debit air bersih menghasilkan perkiraan sebesar 80% air limbah. Nilai Qp pada inlet IPAL 1 sebesar 0,59 m3/detik dengan diameter 900 mm, sedangkan nilai Qp pada inlet IPAL 2 sebesar 1,42 m3/detik dengan diameter 1000 mm. Pengaliran air limbah diusahakan secara gravitasi dengan kedalaman galian maksimum sebesar 6 m. Sistem drainase skala mikro dirancang untuk memenuhi debit penggelontoran. Perhitungan intensitas hujan terpilih menggunakan Metode Sherman. Titik penggelontoran sebanyak 53 titik dengan debit penggelontoran rata-rata sebesar 0,03 m3/detik. Debit saluran drainase rata-rata sebesar 0,25 m3/detik.
ABSTRACT
Sewerage system is an important part of the urban infrastructure. The research objectives were to design a system configuration domestic wastewater sewerage and modify drainage systems in Bogor City for flushing discharge. The research used secondary data from relevant institutions, literature, and the results of previous researches. Estimated of the population of each village in 2035 used geometric method. Wastewater Treatment Plant (WWTP) would be constructed in two locations in Bantarjati and Mekarwangi Village. Planning of services area included 254 blocks and the number of manholes were 334. Clean water which produced peak hours flowrate (Qph) was 5.75 L/sec. Water flowrate produced an estimated of 80% wastewater flowrate. Q peak at the inlet of the WWTP 1 was 0.59 m3/sec with diameter of 900 mm, while Q peak at the inlet of the WWTP 2 was 1.42 m3/sec with diameter of 1000 mm. The stream of wastewater carried out by gravity with the maximum digging depth of 6 m. The system of micro-scale drainage was designed to supply flushing flowrate. Rainfall intensity calculation is done using the Sherman Method with period of 20 years rain repetition. Flushing points were 53 with flowrate average of 0.03 m3/sec. Drainage flowrate average was 0.25 m3/sec. Micro-scale drainage was designed rectangular. Result of the width and height average dimension were 0.43 m and 0.42 m, respectively.
Keywords
Full Text:
artikel lengkap (PDF) (Bahasa Indonesia)References
Analisse, 2009. Cost of Sewage Pumping System. International Journal of Engine Technology, 243:265-272.
Anonim, 2005. Kriteria Perencanaan Sektor Air Bersih. Direktorat Jenderal Cipta Karya, Departemen Pekerjaan Umum, Jakarta.
Anonim, 2011. Tata Cara Rancangan Sistem Jaringan Perpipaan Air Limbah Terpusat tentang Pedoman Perencanaan. Direktorat Jenderal Cipta Karya, Departemen Pekerjaan Umum, Jakarta.
Anonim, 2012. Pencemaran Lingkungan Kota Bogor Tahun 2012. Badan Lingkungan Hidup Kota Bogor, Bogor.
Bose, A.R.J.C., Neelakantan, T.R., dan Mariappan, P., 2012. Peak Factor In The Design of Water Distribution-An Analysis. International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology, 3(2):123-129.
Calvin, K., 2009. Flushing Periode of Sewer System. Journal of Enviromental Engineering, 234(9):124-132.
Chapin, J., 2006. Municipal Wastewater Pump Station Design Problems and Solutions. Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation, 2158-2164.
Gambiro, H., 2012. Pengelolaan Limbah Cair Volume VI. Universitas Mercu Buana, Jakarta.
Ginanjar, Y., 2007. Alternatif Sistem Penyaluran Air Buangan Domestik Kecamatan Garut Kota dengan Sistem “Pipa Riol Kecil”. Skripsi, Program Studi Teknik Lingkungan, Fakultas Teknik Sipil dan Lingkungan ITB, Bandung.
Howard, G., 2009. Design of Manhole Placement. Journal of Civil Engineering, 342:153-162.
Ilmi, N., 2009. Perencanaan Debit Penggelontoran Dalam Sistem Air Limbah. Jurnal Teknik Sipil, 211(2):243-250.
Imam, E.H., dan Elnakar, H.Y., 2014. Design Flow Factors for Sewerage Systems in Small Arid Communities. Journal of Advanced Research, 5(5):537-542.
Imhoff, K., dan Fair, G.M., 1956. Sewage Treatment. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York.
Kerr, J., 2008. Hinton Eco-industrial Park First to Use Sewer System. International Journal of Environment Engineering and Technology, 101:4299.
Novak, P., 2010. Sediment Transport in Smooth Fixed Bed Channels. Journal Hydraulogic Civil Engineering, 101(9):1139-1154.
Okonkwo, G.I., dan Mbajiorgo, C.C., 2010. Rainfall Intensity Method Analysis for South Eastern Nigeria. International Journal of Agricultural Engineering: The CIGR e-Journal, 12:1-15.
Qasim, S.R., 1998. Wastewater Treatment Plants. CRC Press, Boca Raton.
Taheri, B., 2011. Establishment of Intensity-Duration-Frequency Curves for Precipitation. Journal of Hydrology, 347:197– 210.
Rahmawati, F., Oktiawan, W., dan Nugraha, W.D., 2013. Detail Engineering Design (DED) Sistem Penyaluran Air Limbah dan Instalasi Pengolahan Air Limbah Kawasan Industri BSB City, Mijen Kota Semarang. Jurnal Lingkungan, 2(2):1-10 .
Said, M.E., 1992. Probabilistic Design of Open Drainage Channels. Journal Irrigation Drainage Engineering, 118(6):868-881.
Suripin, 2004. Sistem Drainase Perkotaan yang Berkelanjutan. Penerbit Andi, Yogyakarta.
Suroso, 2006. Analisis Curah Hujan Untuk Membuat Kurva Intensity-Duration-Frequency (IDF) di Kawasan Rawan Banjir Kabupaten Banyumas. Jurnal Teknik Sipil, 3(1):37-40.
Thomas, L., 2010. Planning of Hydrolic Piping System. Journal of Civil Engineering, 37:165-173.
Wardhana, A.O., 2013. Perancangan Instrumentasi untuk Perhitungan Standar Deviasi dan Standar Error Barometer Tabung Bourdon. Skripsi, Program Studi Teknik Mesin, Universitas Dipenegoro, Semarang.
Watson, J., 2010. Calculation of Wastewater Discharge on Urban Sewer. Journal of Civil Engineering, 231(3):342-352.
Widiana, S., Wardana, I.W., dan Handayani, D.S., 2013. Perencanaan Teknis Sistem Penyaluran dan Pengolahan Air Buangan Domestik (Studi Kasus: Kelurahan Bojongsalaman Kecamatan Semarang Barat Kota Semarang). Jurnal Teknik Lingkungan, 2(1):1-9.
Willems, P., 2007. Compound Intensity Duration Frequency Relationships of Extreme Precipitation for Two Seasons and Two Storm Types. Journal of Hydrology, 233:189-205.
Yiping, G., 2006. Updating Rainfall IDF Relationships to Maintain Urban Drainage Design Standards. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 11:506-509.
Article Metrics
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Copyright (c) 2017 Jurnal Manusia dan Lingkungan







