VARIASI PERUBAHAN PENGGUNAAN LAHAN PADA BERBAGAI TIPE BENTUKLAHAN DAN KAITANNYA DENGAN ALIRAN DASAR SUNGAI PADA DAS KEDUANG PROVINSI JAWA TENGAH (The Variation of Land-Use Change in Various Landform Type and Its Correlation With River Baseflow)
Bokiraiya Latuamury(1*), Sudarmadji Sudarmadji(2), Slamet Suprayogi(3)
(1) Jurusan Kehutanan, Fakultas Pertanian, Universitas Pattimura, Jl. Ir. M. Putuhena, Poka, Ambon 97123
(2) Jurusan Geografi Lingkungan, Fakultas Geografi, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Sekip Utara, Yogyakarta 55281
(3) Jurusan Geografi Lingkungan, Fakultas Geografi, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Sekip Utara, Yogyakarta 55281
(*) Corresponding Author
Abstract
ABSTRAK
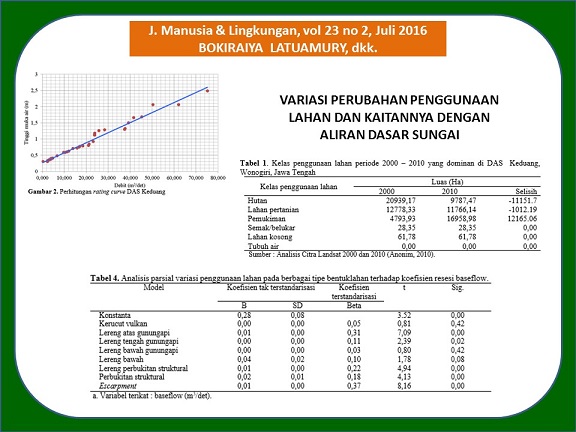
Penelitian variasi penggunaan lahan dan kaitannya dengan aliran dasar skala DAS semakin banyak digunakan, sebagai akibat dari kebutuhan air yang terus meningkat. Karakteristik DAS mempengaruhi proses perubahan curah hujan sebagai masukan, dan aliran sungai sebagai keluaran. Untuk itu penting dilakukan penelitian dengan tujuan untuk menganalisis secara geospasial mengenai variasi perubahan penggunaan lahan pada berbagai tipe bentuklahan dalam kaitannya dengan aliran dasar sungai. Hasil analisis statistik variasi penggunaan lahan pada berbagai tipe bentuklahan dalam kaitannya dengan aliran dasar sungai secara geospasial menunjukkan bahwa ada perubahan yang signifikan. Karakteristik aliran dasar sungai di DAS Keduang Kabupaten Wonogiri Provinsi Jawa Tengah menunjukkan bentuk kurva resesi landai dengan koefisien resesi 0,99 dan volume aliran dasar rata-rata cukup tinggi. Analisis kurva resesi menggambarkan kondisi aliran dasar memiliki kemampuan menyimpan dan meloloskan aliran optimal. Dengan demikian pengelolaan ekosistem sungai secara bersinergi dan berkelanjutan dapat mempertahankan pola pemanfaatan sungai oleh masyarakat sekitar sebagai sebuah alternatif ketersediaan air masyarakat lokal.
ABSTRACT
Nowadays, research that concerning in the relation between land use change and baseflow in watershed scale are increased due to the increasing water demand. Watershed characteristic typically affecting the alteration of rainfall as input and river flow as output. Therefore, this research aims to perform geospatial analysis on the variation of landuse change in various landform type and its correlation with river baseflow. Results from statistical analysis of landuse on the various types of landform and its correlation with river baseflow indicated that there are significant changes. Baseflow characteristic in Keduang watershed, Wonogiri, Central Java Province shows that the shape of recession curve is ramps with coefficient 0,99 and high baseflow average. Recession curve analysis describes that baseflow condition capable in storing and through the optimum flow. Hence, synergic and sustainable river ecosystem management could maintain river utilization pattern by the local community as an alternative for local water supply.
Keywords
Full Text:
ARTIKEL LENGKAP (PDF) (Bahasa Indonesia)References
Anonim, 2008. Analisis Data Debit dengan Sumber Data, Balai Penelitian dan Teknologi Pengelolaan Daerah Aliran Sungai (BPTPDAS) Surakarta, Surakarta.
Anonim, 2010. Analisis Citra Landsat untuk Morfometri DAS Keduang Kabupaten Wonogiri Provinsi Jawa Tengah, Semarang.
Asdak, C., 2002. Hutan dan Perilaku Aliran Air : Klasifikasi Keberadaan Hutan dan Pengaruhnya terhadap Banjir dan Kekurangan Air. Jurnal Manusia dan Lingkungan, 9(1):40–49.
Bloomfield, J.P., dan Griffiths, D.J., 2009. Examining Geological Controls on Baseflow Index (BFI) Using Regresi Analysis: An Illustration from the Thames Basin, UK. Journal of Hydrology, 373:164-176.
Eckhardt, K., 2005. How to Construct Recursive Digital Filters for Baseflow Separation? Hydrological Processes, 19:507–515.
Longobardi, A. dan Villani P., 2008. Baseflow Index Regionalization Analysis in a Mediterranean Area and Data Scarcity Context : Role of The Catchment Permesbility Index. Journal of Hydrology, 355:63–75.
Nathan, R.J., dan McMahon, T.A., 1990. Evaluation of Automated Techniques for Base Flow and Recession Analysis. Water Resources Research, 26(7):1465-1473.
Pontius, R.G. dan Schneider,L.C., 2001. Land-cover change model validation by an ROC method for the Ipswich watershed, Massachusetts, USA. Agriculture, Ecosystem and Environment. 85:239-248.
Seyhan, E. 1990. Dasar-Dasar Hidrologi. Gadjah Mada University Press. Yogyakarta.
Szilagyi, J., Gribovszki, Z., dan Kalicz, P., 2007. Estimation of Catchment-Scale Evapo-transpiration from Baseflow Recession Data: Numerical Model and Practical Application Results. Journal of Hydrology 336: 206–217.
Tallaksen, L.M., 1994. A Review of Baseflow Recession Analysis. Journal of Hydrology, 165:349-370.
Turner, M.G., Gardner, R.H., dan O’Neill, R.V., 2001. Landscape Ecology in Theory and Practice Pattern and Process. Springer-Verlag, New York, 401.
Verburg, P.H., van Eck, J.R., de Hijs, T.C., Dijst, M.J., dan Schot, P., 2004. Determination of Land Use Change Patterns in the Netherlands. Journal of Environmental Planning, 31:125–150.
Wittenberg, H., dan Sivapalan, M., 1999. Watershed Groundwater Balance Estimation using Streamflow Recession Analysis and Baseflow Separation. Journal of Hidrology, 219:20-33.
Yu-Pin, L., Nien-Ming, H., Pei-Jung, W., Chen-Fa, W., dan Verbur, P.H., 2007. Impacts of Land Use Change Scenarios on Hydrology and Land Use Patterns in the Wu-Tu Watershed in Northern Taiwan. Landscape and Urban Planning, 80:111-126.
Zhang, Y.K., and Schilling, K.E., 2005. I Streamflow and Baseflow in Mississippi River Since the 1940 s: Effect of Land Use Change. Journal of Hydrology, 324:412-422.
Article Metrics
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Copyright (c) 2017 Jurnal Manusia dan Lingkungan







