COMMUNITY ENGAGEMENT WITH URBAN RIVER IMPROVEMENT: THE CASE OF YOGYAKARTA CITY (Melibatkan Masyarakat dalam Memperbaiki Lingkungan Sungai Perkotaan : Kasus Kota Yogyakarta)
Hari Kusnanto(1*), Suprapto Dibyosaputro(2), Suwarno Hadisusanto(3), Sri Puji Saraswati(4)
(1) Center for Environmental Studies, Universitas Gadjah Mada Jl. Lingkungan Budaya, Sekip Utara Yogyakarta, 55281
(2) Center for Environmental Studies, Universitas Gadjah Mada Jl. Lingkungan Budaya, Sekip Utara Yogyakarta, 55281
(3) Center for Environmental Studies, Universitas Gadjah Mada Jl. Lingkungan Budaya, Sekip Utara Yogyakarta, 55281
(4) Center for Environmental Studies, Universitas Gadjah Mada Jl. Lingkungan Budaya, Sekip Utara Yogyakarta, 55281
(*) Corresponding Author
Abstract
ABSTRACT
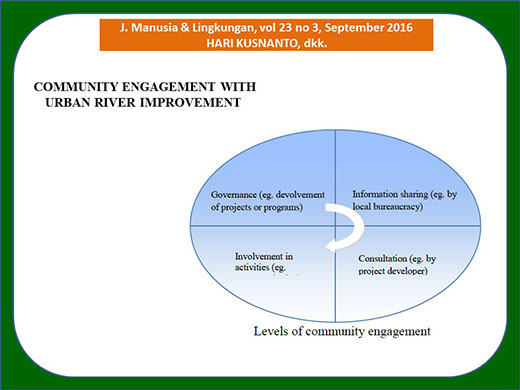
The restoration of urban rivers has shifted from predominantly physical and ecological to community oriented social and economic improvement. Community engagement is needed in the people approach of development. Information sharing and public consultation are not enough. A case study among the riverside communities living in Yogyakarta city indicated that these communities need to move out of poverty and destitution through coaching and mentoring by various experts, and at the same time they would assure the ecosystem functioning of urban rivers.
ABSTRACT
Restorasi sungai-sungai perkotaan telah bergeser dari peningkatan fisik dan ekologis menjadi lebih berorientasi pada sosial dan ekonomi. Keterlibatan masyarakat dibutuhkan dalam pendekatan manusiawi pembangunan. Pemberian informasi dan konsultasi public tidak cukup studi kasus pada komunitas-komunitas yang hidup di pinggir sungai di kota Yogyakarta menunjukkan bahwa komunitas tersebut perlu mengentaskan diri dari kemiskinan dan keterbelaknagn dengan bantuan ahli, dan pada saat yang sama menjaga fungsi ekosistem sungai-sungai perkotaan.
Keywords
Full Text:
ARTIKEL LENGKAP (PDF)References
Bell, K.B., Lindenfeld, L., Speers, A.E., Teisl, M.F., and Leahy, J.E., Creating Opportunity for Improving Lake-Focused Stakeholder Engagement: Knowledge-Action Systems, Pro-Environment Behavior and Sustainable Lake Management. Lakes & Reservoirs: Research and Management, 18:5-14.
Firman, T., 2004. Major Issues in Indonesia’s Urban Land Development. Land Use Policy ,21:347-355.
Frazer, L., 2005. Paving Paradise: The Peril of Impervious Surfaces. Environmental Health Perspectives, 114(1):A21.
Lange, C., Schneider, M., Mutz, M., Haustein, M., Halle, M., Seidel, M., Sieker, H., Wolter, C., Hinkelmann, R., 2015. Model-Based Design for Restoration of A Small Urban River. Journal of Hydro-environment Research, 9(2):226-236.
Lu, Y., 2010. Rural-Urban Migration and Health: Evidence from Longitudinal Data in Indonesia. Social Science and Medicine, 70(3):412-419.
Minnery, J., Argo, T., Winarso, H., Hau, D., Veneracion, C.C., Forbes, D., and Childs, I., 2013. Slum Upgrading and Urban Governance: Case Studies in Three South East Asian Cities. Habitat International, 39:162-169.
Sakundarno, M., Bertolatti, D., Maycock, B., Spickett, J., and Dhaliwai, S., 2014. Risk Factors for Leptospirosis Infection in Humans and Implications for Public Health Intervention in Indonesia and the Asia-Pacific Region. Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health, 26(1):15-32.
Setiawan, B., 2002. Community Initiatives and Involvement in Creating Healthy and Friendly Cities: Lessons from Yogyakarta, Jurnal Manusia dan Lingkungan, 9(1):1-15.
Tinglanchali, T., 2012. Urban Flood Disaster Management, Procedia Engineering, 32(1):25-37.
Tunas, D., and Peresthu A., 2010. The Self-Help Housing in Indonesia: The Only Option for The Poor? Habitat International, 34:315-322.
Widodo, J., 2012. Urban Environment and Human Behavior: Learning from History and Local Wisdom. Procedia, 42:6-11.
Zhu, Y., 2015. Toward Community Engagement: Can The Built Environment Help? Grassroots Participation and Communal Space in Chinese Urban Communities. Habitat International, 46:44-53.
Article Metrics
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Copyright (c) 2017 Jurnal Manusia dan Lingkungan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.







