DIFFERENCE IN PERCEPTION OF URBAN GREEN SPACES BETWEEN DANCHI AND APARTMENT RESIDENTS IN TOKIWADAIRA, MATSUDO CITY, JAPAN (Perbedaan dalam Persepsi Ruang Hijau Perkotaan di antara Penghuni Kompleks Rumah Susun dan Apartemen di Tokiwadaira, Kota Matsudo, Jepang)
Prita Indah Pratiwi(1*), Minseo Kim(2), Katsunori Furuya(3)
(1) Landscape Architecture Program, Graduate School of Horticulture, Chiba University, 648 Matsudo Matsudo-shi Chiba 271-8510 Japan.
(2) Landscape Architecture Program, Graduate School of Horticulture, Chiba University, 648 Matsudo Matsudo-shi Chiba 271-8510 Japan.
(3) Landscape Architecture Program, Graduate School of Horticulture, Chiba University, 648 Matsudo Matsudo-shi Chiba 271-8510 Japan.
(*) Corresponding Author
Abstract
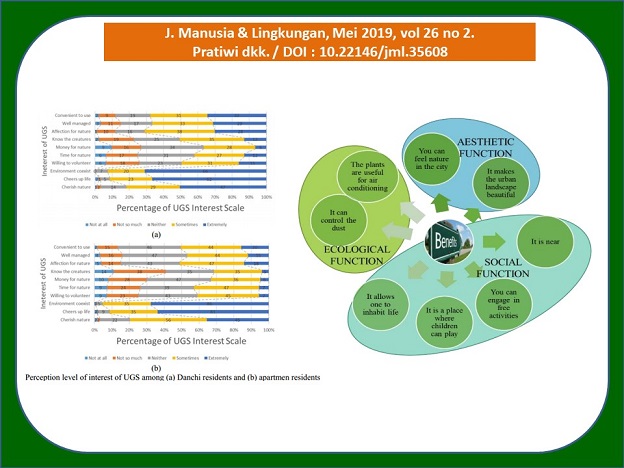
In Japan, where most of the population now comprises elderly people, various social problems have emerged, including lack of workers, inadequate care for elderly people, lower birthrate, the abandonment of local areas, and lack of community. In highly populated urban areas, city planners propose sustainable landscape planning but sometimes ignore the public, eliminating their sense of place. This study aimed to clarify the differences in green space perception between residents of danchi and apartments in Tokiwadaira, Matsudo, to learn what residents’ attributes may influence their perceptions, and to formulate factors of recognition and awareness of urban green spaces. The research was conducted in three stages: a recognition and awareness survey, analysis, and interpretation. A Mann-Whitney U test and Welch’s t test were applied to examine significant differences in perception level; a Chi-square test was applied to examine the relationship between residents’ attributes and volunteering activity; finally, factor analysis was applied to characterize residents’ recognition and awareness of nature and green spaces. The results demonstrated three significant differences regarding the benefits of green spaces between danchi and apartment residents, and five significant differences in their interest in green spaces. The attributes influencing danchi residents’ perceptions were gender and age, while those influencing apartment residents were age, existence of children, employment status, length of stay, and existence of green spaces. The three factors accounting for residents’ interest in green spaces and nature were: high recognition and awareness, moderate recognition and awareness, and low recognition and awareness. The results may prove useful as guidance for specific local governments in relation to urban green space planning and design.
Abstrak
Di Jepang di mana sebagian besar penduduknya terdiri atas orang lanjut usia, berbagai masalah sosial telah terjadi, seperti kurangnya tenaga kerja, perawatan bagi orang lanjut usia yang rendah, kelahiran anak-anak yang rendah, terabaikannya daerah setempat, dan kurangnya komunitas. Di daerah perkotaan yang berpenduduk padat, perencana kota mengusulkan perencanaan lanskap berkelanjutan, tetapi terkadang mengabaikan publik dan menghilangkan makna tempat mereka. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk memperjelas perbedaan persepsi ruang hijau antara penghuni di kompleks rumah susun semi publik dan apartemen di Tokiwadaira, Matsudo, untuk mengetahui atribut penghuni yang dapat mempengaruhi persepsi mereka, dan untuk merumuskan faktor-faktor pengenalan dan kesadaran akan ruang hijau perkotaan. Penelitian ini dilakukan dalam tiga tahap: survei kesadaran dan pengenalan, analisis, dan interpretasi. Uji Mann-Whitney U dan Welch's t digunakan untuk menguji perbedaan level persepsi yang signifikan antara penghuni danchi dan apartemen. Uji Chi-square digunakan untuk menguji hubungan antara atribut penghuni dan kegiatan sukarela, terakhir analisis faktor digunakan untuk mengkarakterisasi pengenalan dan kesadaran penghuni terhadap alam dan ruang hijau. Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa terdapat tiga perbedaan signifikan mengenai manfaat ruang hijau di antara penghuni danchi dan apartemen, dan lima perbedaan signifikan terhadap minat ruang hijau. Atribut yang mempengaruhi persepsi penduduk danchi adalah gender dan usia, sedangkan hal-hal yang mempengaruhi penghuni apartemen adalah usia, keberadaan anak, status pekerjaan, lama tinggal, dan keberadaan ruang hijau. Tiga faktor yang menentukan minat penghuni terhadap alam dan ruang hijau di antaranya: pengenalan dan kesadaran yang tinggi, pengenalan dan kesadaran yang sedang, serta pengenalan dan kesadaran yang rendah. Hasil penelitian ini dapat berguna sebagai panduan perencanaan dan desain ruang hijau kota untuk pemerintah lokal.
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFReferences
Bell, K.B., Lindenfeld, L., Speers, A.E., Teisl, M.F., and Leahy, J.E., 2013. Creating Opportunity for Improving Lake-Focused Stakeholder Engagement: Knowledge-Action Systems, Pro-Environment Behavior and Sustainable Lake Management. Lakes & Reservoirs: Research and Management. 18:5-14.
Elias, N., 1983. Die hofische Gesselschaft. Suhrkamp. Frankfurt.
Fraenkel, J.R., and Wallen, N.E., 1993. How to Design and Evaluate Research in Education. McGraw-Hill Inc. Singapore.
Hidayat and Istiadah., 2011. Panduan Lengkap Menguasai SPSS 19 untuk Mengolah Data Statistik Penelitian. Media Kita. Jakarta.
Karan, P.K., 2004. Japan in the 21st Century: Environment, Economy, and Society. The University Press of Kentucky. Kentucky.
Kim, M., Rupprecht, C.D.D., and Furuya, K., 2017. Spatial Typology in Informal Urban Green Spaces: The Case of Ichikawa City, Japan. In: Program Book of Japan Geosciences Union Meeting 2017. Chiba, 20–25 May 2017.
Kusnanto, H., Dibyosaputro, S., Hadisusanto, S., and Saraswati, S.P., 2016. Community Engagement With Urban River Improvement: The Case of Yogyakarta City. J. Manusia & Lingkungan. 23(3):390-393.
Lucas, O.W.R., 1991. The Design of Forest Landscape. Oxford University Press. New York.
Meltzer, G., 2000. Cohousing: Verifying the Importance of Community in the Application of Environmentalism. Journal of Architecture and Planning Research. 17(2):110-132.
Mulyati, A., Soewarno, N., Ronald, A. and Sarwadi, A., 2016. Karakteristik Spasial Permukiman Vernakular Perairan di Sulawesi Tengah. J. Manusia & Lingkungan. 23(1):122-128.
Othman, A.R., dan Fadzil, F., 2014. Influence of Outdoor Space to the Elderly Wellbeing in a Typical Care Centre. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences. 170:320-329.
Pleson, E., Nieuwendyk, L.M., Lee, K.K., Chaddah, A., Nykiforuk, C.I.J., and Schopflocher, D., 2014. Understanding Older Adults’ Usage of Community Green Spaces in Taipei, Taiwan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 11:1444-1464.
Pratiwi, P.I., Furuya, K. and Sulistyantara, B., 2014a. The Difference in People's Response Toward Natural Landscape Between University Students of Japan and Indonesia. J. Manusia & Lingkungan. 21(2):247–253.
Pratiwi, P.I., Sulistyantara, B., Gunawan, A., and Furuya, K., 2014b. A Comparative Study on the Perception of Forest Landscape Using List Method Between University Students of Japan and Indonesia. Jurnal Managemen Hutan Tropika. 20(3):167-178.
Ronald, R., and Alexy, A., 2011. Home and Family in Japan. Routledge, Taylor and Francis Group. London.
Roscoe, J., 1975. Fundamental Research Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences. Holt, Rinehart, & Winston. New York.
Ross, S., and Wall, G., 1999. Evaluating Ecotourism: The Case of North Sulawesi, Indonesia. Tourism Management. 20(6):673–682.
Sinery, A.S., Manusawai, J., 2016. Partisipasi Masyarakat Dalam Program Pengelolaan Hutan Lindung Wosi Rendani. J. Manusia & Lingkungan. 23(3):394-401.
Sulistyantara, B. and Pratiwi, PI., 2011. Perencanaan Penataan Lanskap Kawasan Wisata dan Penyusunan Alternatif Program Wisata di Grama Tirta Jatiluhur, Kabupaten Purwakarta, Provinsi Jawa Barat. Jurnal Lanskap Indonesia. 3(2):58-65.
Article Metrics
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Copyright (c) 2019 Jurnal Manusia dan Lingkungan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.







